Storage
Natural gas is extracted continuously throughout the year, whereas the amount consumed depends on times and seasons. On a winter’s day, gas consumption may be eight times as much as on a summer's day. There are also significant fluctuations throughout the day.
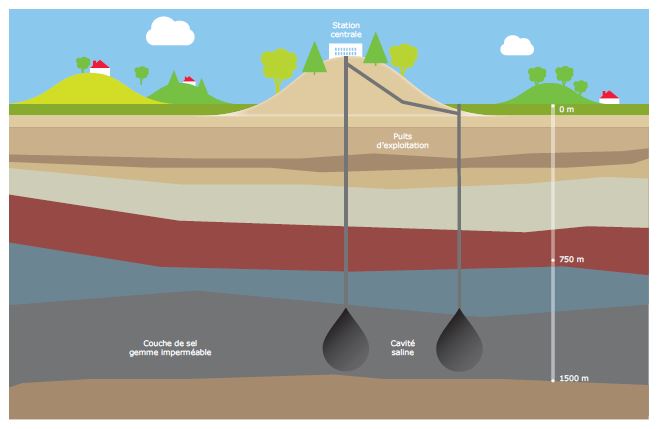
 Storage capacities in salt cavities
Storage capacities in salt cavities
Storage enables a form of energy to be kept for later use; gas surpluses received in summer are stockpiled for use during cold weather in winter.
Underground geological structures are often used for seasonal storage. Airtight cavities emptied of water or salt are used for the storage of injected natural gas. Another option is to create an artificial rock cavern.
The largest aquifer reservoir in Chemery, France, can hold 7 billion m3 of natural gas, which is equivalent to twice Switzerland’s annual gas consumption. Gaznat has storage capacities in salt cavities in the Bourg-en-Bresse region of France.
Storage capacities are a strategic asset to the company; in particular, they enable Gaznat to cover a third of peak-level consumption in the winter period. Direct access to storage helps ensure optimal continuity of supply.
It is also possible to use liquefied natural gas reservoirs for seasonal storage.
In order to smooth out daily or weekly peaks in consumption, buried pipes are normally used for storage, such as at Volketswil, in the canton of Zurich.