Gas year
A gas year is the time span between October 1 of a given year at 6:00 am and October 1 of the following year at 6:00 am.
Traditionally, the gas year is offset from the accounting year because contracts were negotiated before the cold weather arrived.
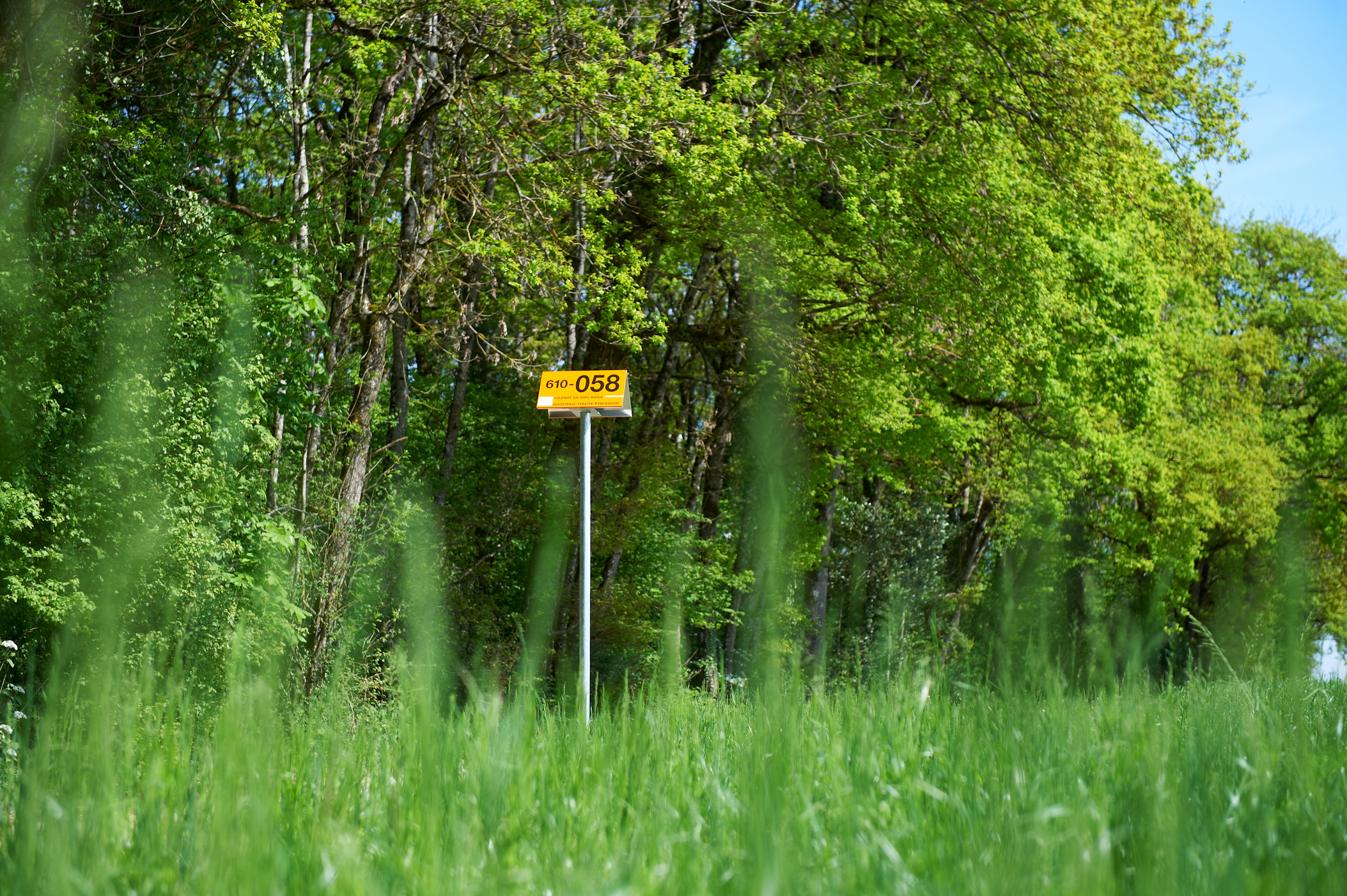
Marker post
Orange signpost, about 2.50 to 3 metres high, which enables the path of an underground pipe to be tracked either at ground level or from the air (e.g. from a helicopter).
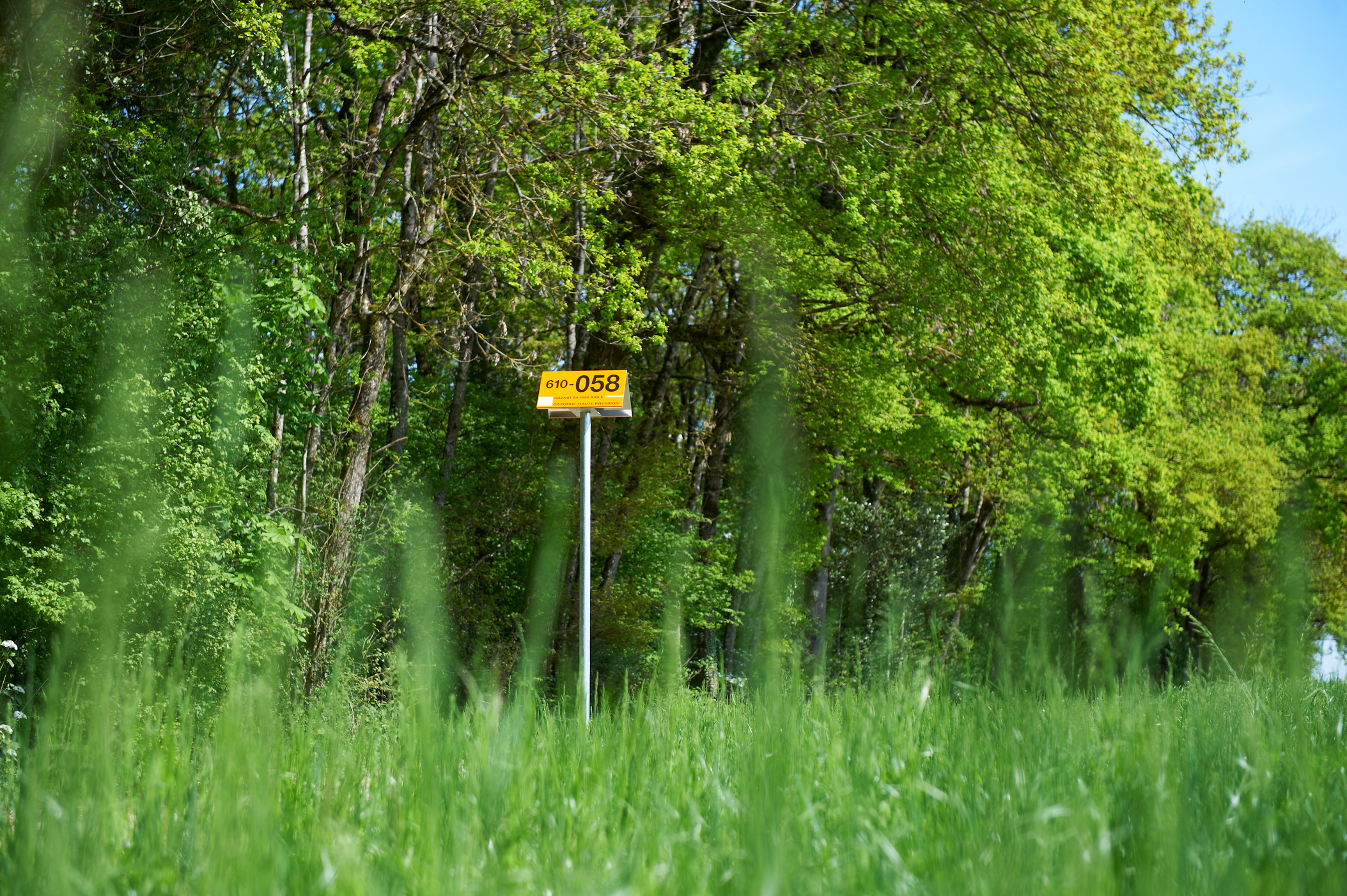

Marker posts form an integral part of pipeline transportation installations.
Bar
Unit of measurement of fluid pressure.
The unit of pressure derived from the International System of Units (SI) is the pascal (Pa). The Pascal is the uniform pressure that exerts a total force of one newton perpendicularly upon a plane surface of one square metre.
1 bar corresponds to 100,000 Pa, or about 1 kg/cm2. Normal atmospheric pressure, for example, is around 1 bar. Gas is delivered to the end consumer (e.g. for a boiler) at 20 millibars.
Biogas
Gas produced by the fermentation of animal or vegetable organic materials in the absence of oxygen. This fermentation, which is also known as methanisation, occurs naturally in swamps and spontaneously in dumps containing organic waste.
Network capacity
The networks capacity to transport a certain hourly volume of natural gas, from the injection point to the delivery point. This capacity is stated in nm3/h.
“Since gas is compressible, it is possible to change the volume of a given amount of gas by compressing it or changing its temperature. It is therefore impossible to know the mass of a quantity of gas based on its volume without giving the pressure and temperature of the gas at the time when the volume was measured.
It would be unnecessarily complicated to give a temperature and pressure every time a volume of gas is mentioned, so the temperature and pressure at the time when the volume was measured are standardised to “normal” conditions. This is called normal m3”.
Definition adapted from www.mecaflux.com
Cornaux power station
Combined-cycle gas turbine plant (gas turbine and steam turbine) that generates electricity.
CO2
CO2, also known as carbon dioxide or carbonic gas, is a colourless, inert, non-toxic gas.
Its natural sources are numerous: volcanic eruptions, plant, animal and human respiration, forest fires, decomposition of organic material, combustion, etc.
Due to human activity, CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere are increasing every year by an average of 0.5%, which represents a 30% increase over the last two centuries. It is the main greenhouse gas.
Cogeneration
Cogeneration is a method of producing electricity and heat simultaneously.
Congestion
Saturation of the gas transportation network that limits the opportunity for commercial transactions. This regularly occurs at the borders between the European countries, and partly accounts for the persistent differences in market prices in Europe.
Interruptible consumer
Generally, these are consumers who are able to switch to an energy other than gas if necessary. A fuel switch is made at the request of the gas distributor or transporter.
Gas volume corrector
Device which converts the volume measured by a gas meter into a volume of gas under normal conditions (1.01325 bar abs./0°C).
Rate per hour
Quantity of natural gas transported per full hour, expressed in Nm3/h.
Density
The ratio of the masses of two equal volumes of gas and air, each under identical reference conditions. Gases lighter than air have a density lower than 1 and gases heavier than air have a density higher than 1.
Local distribution company
A local distribution company (also called a local gas utility) delivers natural gas to end-use customers.
Scraper station
Allows to send and receive the pistons. Located at each end of the natural gas pipeline when changing sections.
Coalbed methane
It is a gas naturally contained in coal and usually burned or released into the atmosphere during its extraction. Its industrial exploitation would allow for greater energy efficiency in coal mining and a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Natural gas
Natural gas is the least polluting of the so-called fossil fuels, it is a mixture of hydrocarbons naturally present in porous rocks in gaseous form. It is composed mainly of methane (between 81 and 97%). Natural gas is colorless and odorless. For safety reasons, however, a chemical odorant is added to it in order to detect it in case of a leak.
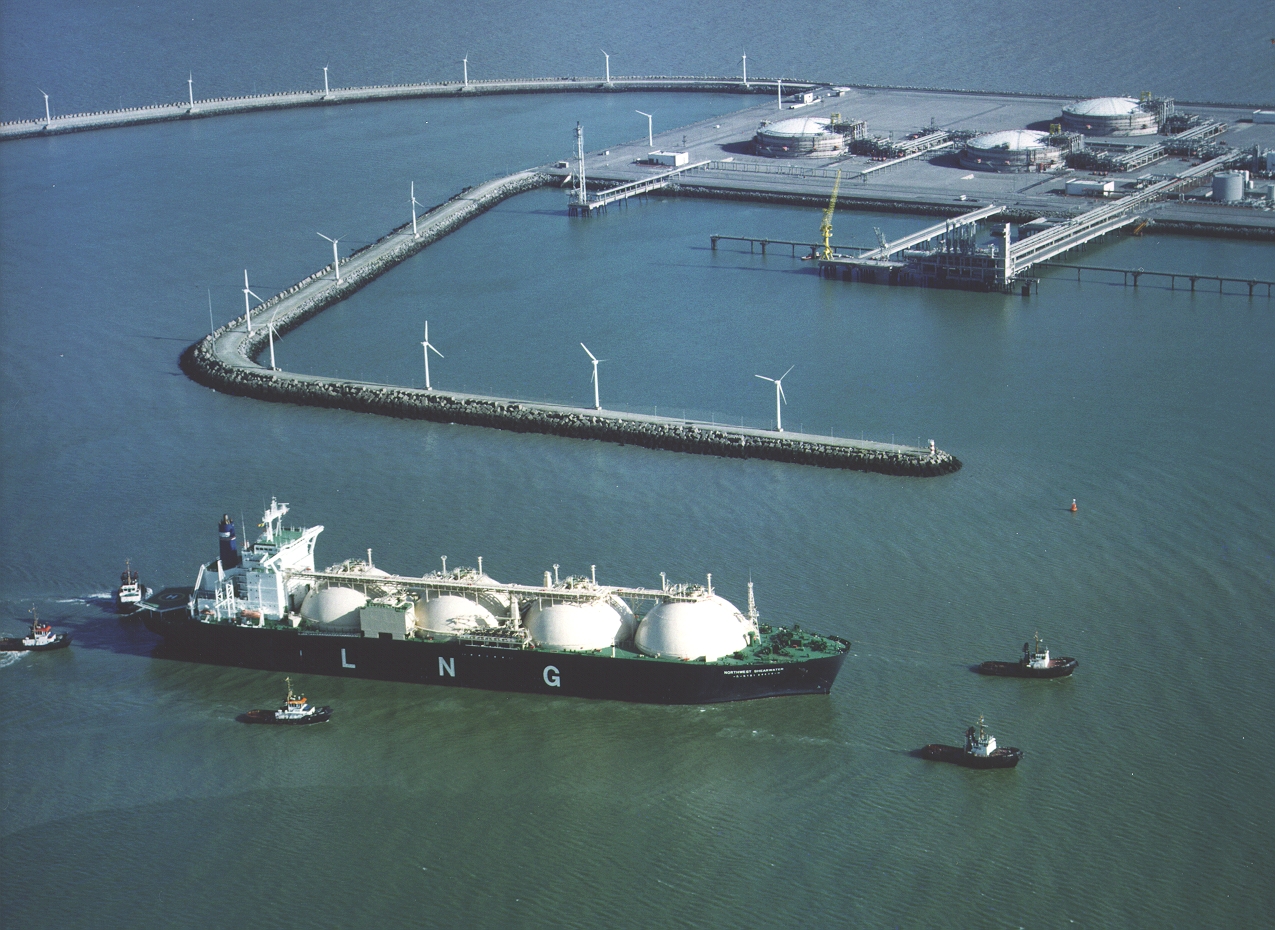
Liquefied Natural Gas - LNG
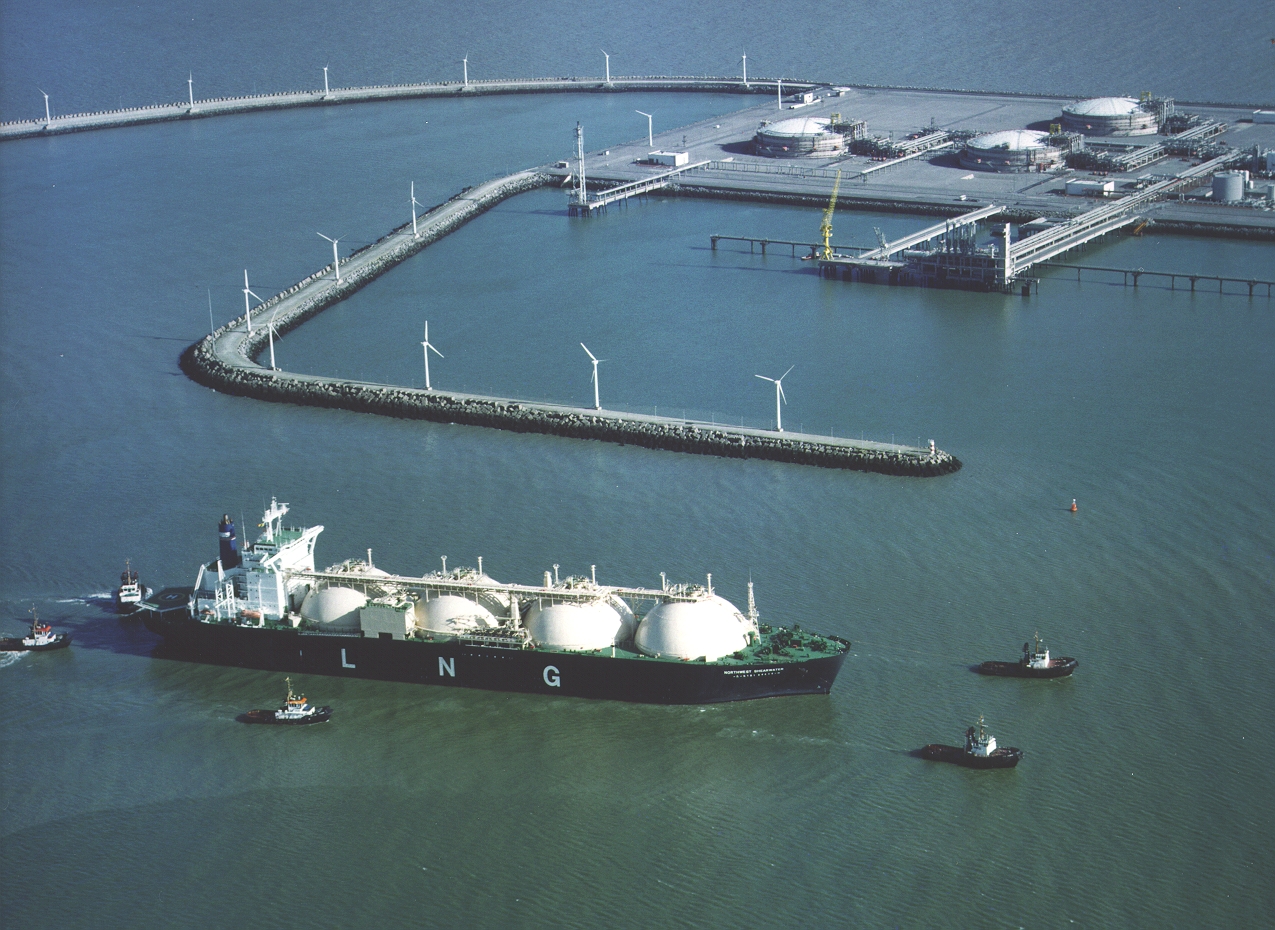

Liquefied natural gas is natural gas condensed in a liquid state. At the port of shipment, the natural gas is liquefied by successive expansion and cooling (to -163°c). Its volume is then reduced by 600 times. The LNG tankers then take care of its transport. At its destination, the LNG is stored in insulated tanks, then transformed by evaporation and injected in gaseous form into land-based pipelines.
Unconventional gas
Unconventional gases include tight gas, shale gas and coalbed methane.
Read more: ScienceDirect
Natural Gas Pipeline
A gas pipeline is intended for the transport of gaseous materials under pressure. It is used to transport natural gas between extraction areas and consumption or export areas. The gas is transported at high pressure (from 16 to more than 100 bar) from the field processing sites or storage facilities. The transport networks includes not only pipelines but also :
— Compressor stations located every 80 to 250 km to maintain the pressure of the gas transported and to ensure its progress in the pipelines;
— Interconnection stations, which are important nodes in the transmission network;
— Delivery stations which ensure the delivery of natural gas to the networks downstream of the distribution system. These stations generally perform the functions of expansion, reheating, filtering and metering of the gas. Gas pipelines are made of butt-welded steel pipes, covered with an insulating material (polyethylene) to help protect them from corrosion. They can be hot-bent (in the factory) or cold-bent (when installed in the field).
An alternative form of transportation can be in liquid form. Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is then transported by LNG tankers.
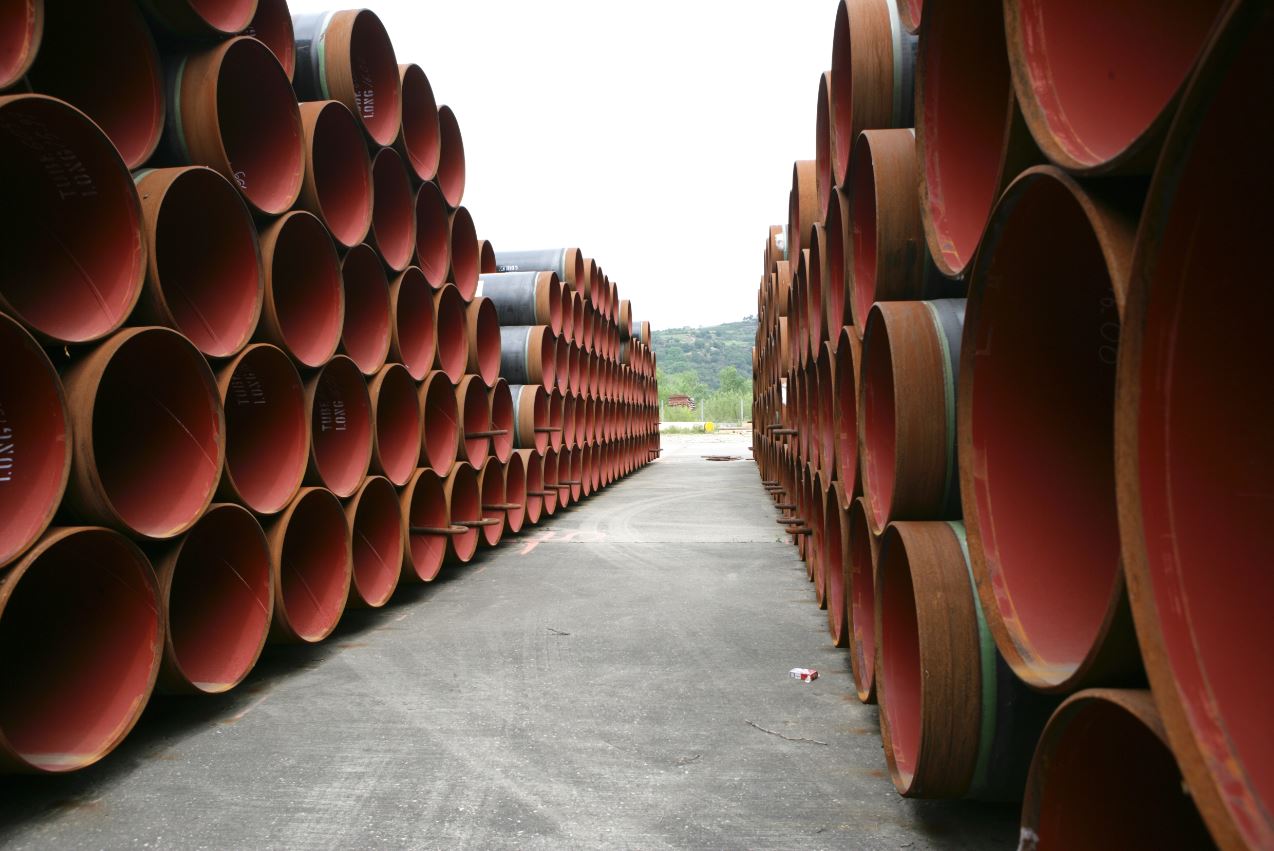

Gas pipelines before installation in the ground
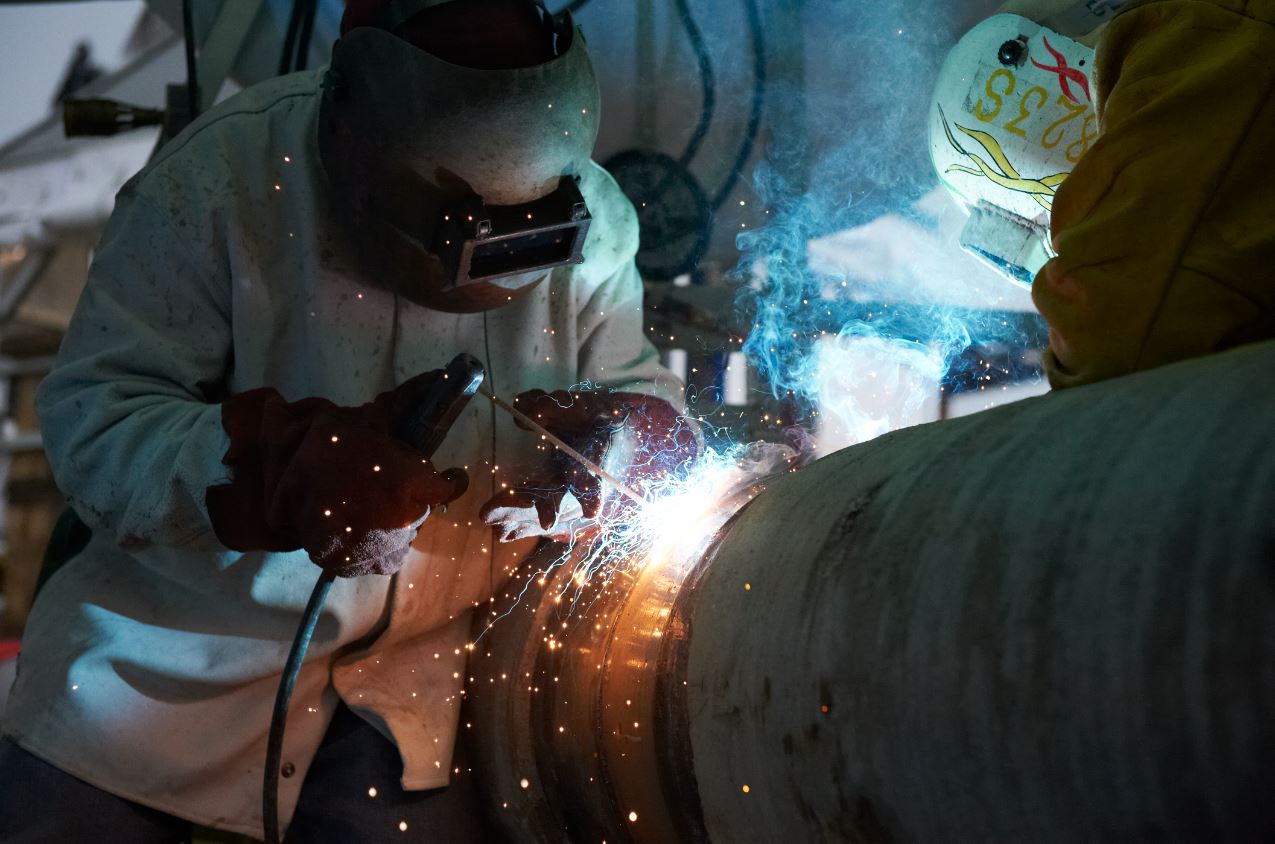

Welding
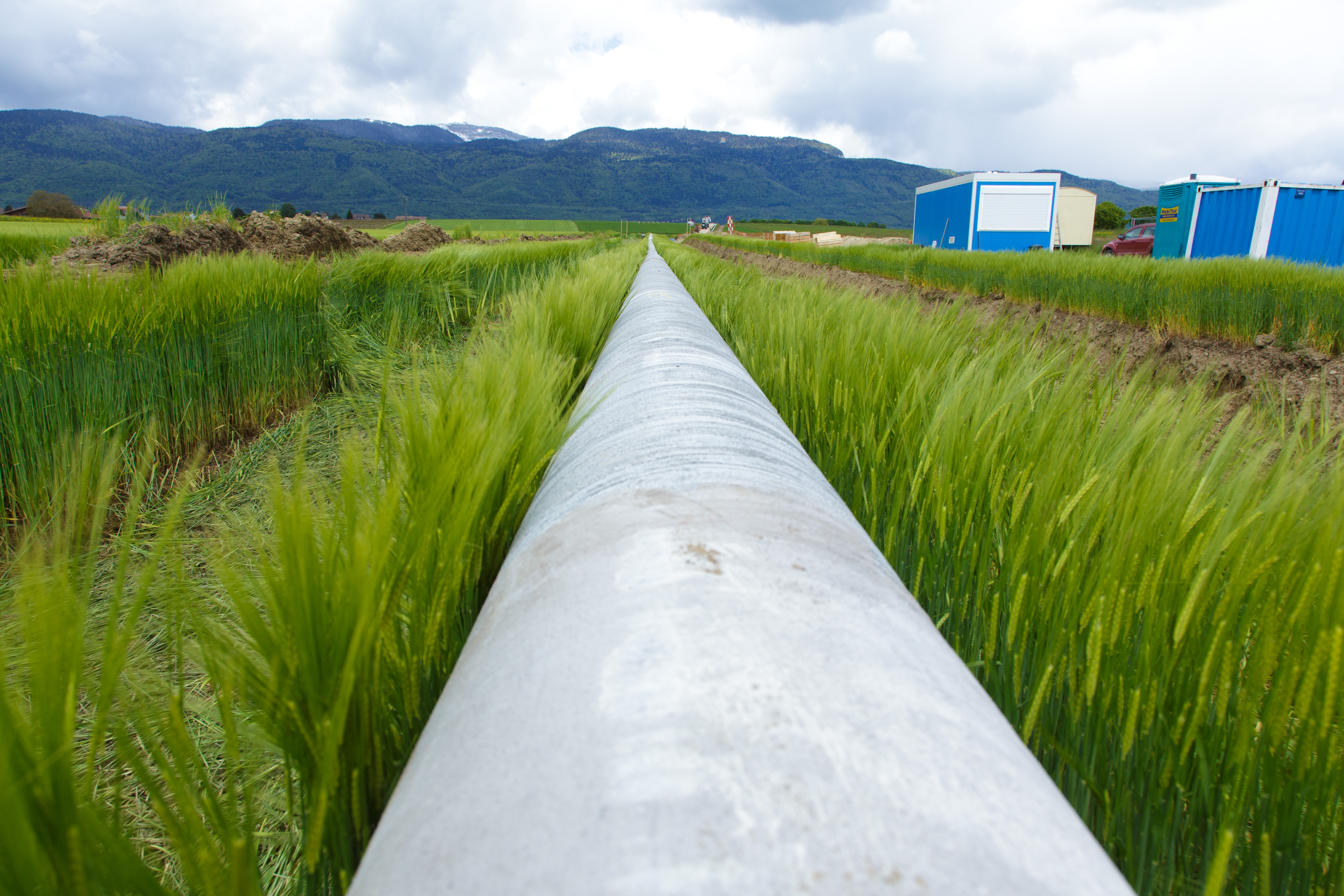

Gas pipeline before laying
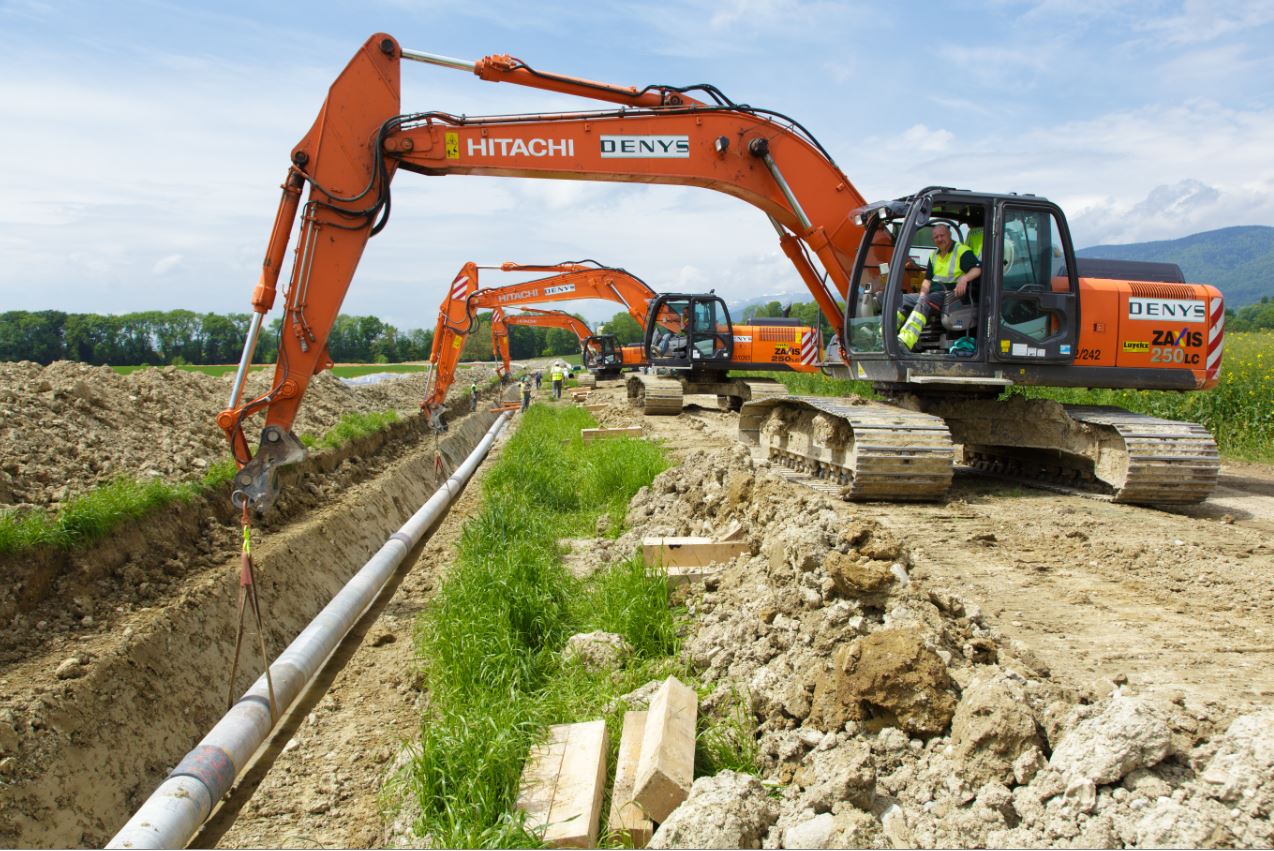

Laying the pipeline

Pipeline after laying,
merely the marker remains visible to indicate the route
LPG - Liquefied petroleum gas
Liquefied petroleum gas is a mixture of light hydrocarbons stored in a liquid state. It is produced by refining oil. It can also be found in its original state in certain fields.
GTC - Trélex - Colovrex Gas Pipeline
The Trélex – Colovrex gas pipeline was officially opened on 9 May 2014 to consolidate security of supply for western Switzerland and respond to growing demand for natural gas in the Geneva region.
Watch the explanatory video about the construction of the Trélex-Colovrex Gas Pipeline (available in French).
Futures market
A market in which transactions give rise to payment and delivery at a later date.
Spot market
A market on which transactions take place at very short notice, typically for the same day (within-day) or for the next day (day-ahead) on the gas and electricity markets.
LNG carrier / Tank ship
Vessel designed to transport natural gas in liquid form.

Offshore (drilling)
Offshore drilling
Onshore (drilling)
Onshore drilling. Also called land-based drilling.
Storage
Natural gas is extracted continuously throughout the year, while its consumption depends on the time of day and the season.
On a winter day, gas consumption can be up to 8 times higher than on a summer day. Fluctuations within a single day are also significant.
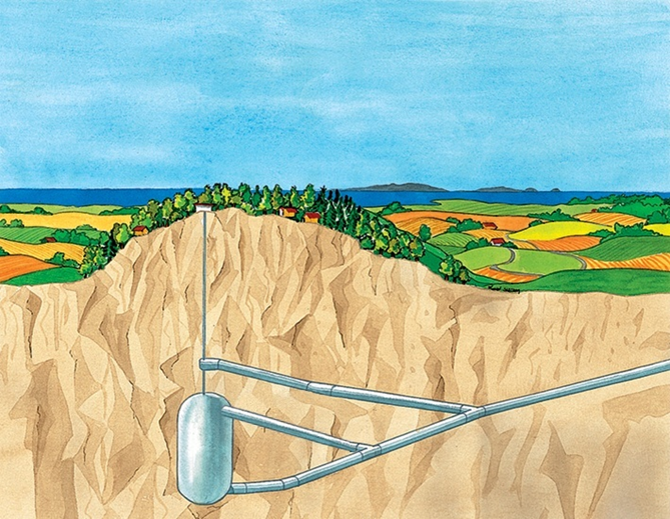
LRC (Lined Rock Cavern) Natural Gas Storage Project
Storage allows energy to be held in reserve for later use; excess gas received in the summer is put in reserve to be available in the winter, during cold periods.
For seasonal storage, underground geological structures are often used. Their watertight cavities, emptied of water or salt, are used to store the injected natural gas. Another variant is to create an artificial rock cavity.
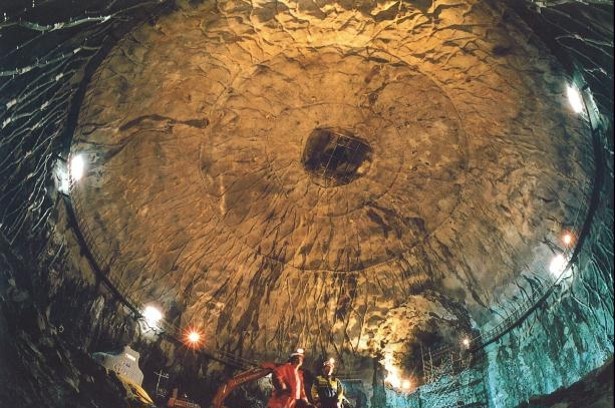

Underground natural gas storage - Cavern
Gaznat has salt cavern storage capacity in Etrez, in the Bourg-en-Bresse region (France).
The storage capacities are a strategic asset for the company; they enable Gaznat to cover approximately one third of its peak consumption during the winter period.
Direct access to storage helps to ensure optimal security of supply.
It is also possible to ensure seasonal storage with liquefied natural gas tanks.
In order to reduce daily or weekly consumption peaks, piped storage in the form of underground pipes is generally used.
Transitgas
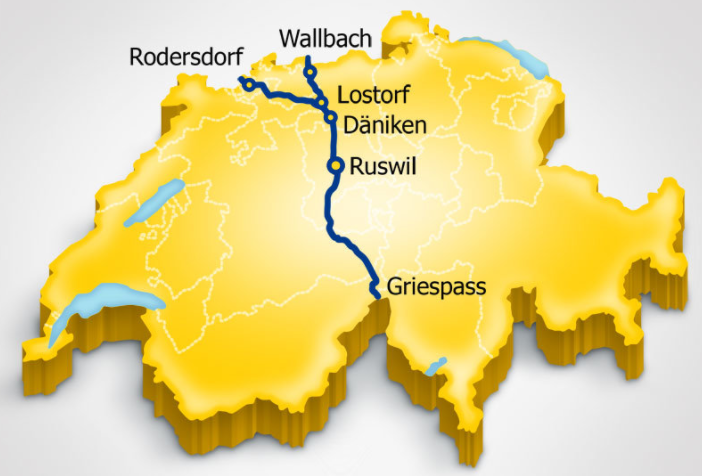
Transitgas is the name given to the natural gas pipeline that crosses the whole of Switzerland from north to south. With a length of 292 km, it connects Germany to Italy.
Dispatching
A control and monitoring center that manages gas movements and the integrity of the gas pipelines on a continuous basis. The network operators work day and night at the dispatching center to ensure that the gas networks are under control 24 hours a day.

Drone
Drones are used in order to monitor the integrity of the gas pipelines. They allow to monitor the condition of the pipelines, in addition to the checks carried out every two weeks by helicopter and cars directly on the ground.
Watch the video explaining the use of the drone to monitor the route of the gas pipelines.
Spot market
A market in which commodities are sold for cash and delivered promptly when the transaction is settled, and other non-financial markets, such as futures markets for commodities.
EFET (European Federation of Energy Traders)
The European Federation of Energy Traders is an association whose aim is to encourage and facilitate energy trading in Europe in the context of open, transparent and liquid wholesale markets.
The organization is actively involved in improving the conditions for energy trading in Europe and in developing a liquid and sustainable European energy market.
EFET currently represents over 90 trading companies in more than 27 European countries.
Read more : EFET
TTF (Title Transfer Facility)
The Title Transfer Facility (TTF) is a Dutch virtual trading point for natural gas.
NCG (NetConnect Germany)
NetConnect Germany, or NCG, is Germany's Virtual Trading Point for gas.
Henry Hub
The Henry Hub is the natural gas distribution center located in Erath, Louisiana.
Physically, it is a set of compressors that distribute gas between several pipelines.
It is particularly important because it serves as a reference point for calculating the price of natural gas futures contracts in the United States and around the world.
Read more: eia
NBP (National Balancing Point)
The National Balancing Point, commonly referred to as the NBP, is a virtual trading location for the sale and purchase and exchange of UK natural gas.
PEG (Point d'Echange de Gaz)
"The exchanges on the wholesale natural gas market take place on virtual points of the French gas transmission network called Gas Exchange Points (PEG). These points are used for exchanges between gas suppliers and for the supply of gas to gas transmission system operators for daily balancing. There is a PEG in each of the French network's market zones: the PEG North and the TRS (Trading Region South, which groups together the balancing zones of GRTgaz South and Teréga). On November 1, 2018, the two marketplaces 〈merged〉 to form the TRF (Trading Region France)."
Source: French Energy Regulatory Commission
THE - Trading Hub Europe
Trading Hub Europe GmbH was established on 1 June 2021 by the network companies bayernets GmbH, Fluxys TENP GmbH, GASCADE Gastransport GmbH, Gastransport Nord GmbH, Gasunie Deutschland Transport Services GmbH, GRTgaz Deutschland GmbH, Nowega GmbH, ONTRAS Gastransport GmbH, Open Grid Europe GmbH, terranets bw GmbH and Thyssengas GmbH.
Since 1 October 2021, Trading Hub Europe is the market area manager for the entire German market area and operates the market area as provided by the Agreement on cooperation pursuant to Section 20 1b) EnWG between operators of gas supply networks located in Germany ("Cooperation Agreement").
PSV - Punto di Scambio Virtuale
Italy's Virtual Trading Point.
"A virtual point located between the entry and exit points of the national gas transportation network, where users and other authorised parties may, on a daily basis, exchange and sell gas injected into the network."
Source : Snam
LNG Terminal Wilhelmshaven (LTeW)

Read more about the German terminal
CEGH - Central European Gas Hub
CEGH is the operator of the Virtual Trading Point in Austria.
Read more: CEGH
TENP - Trans Europa Naturgas Pipeline
"The TENP-pipeline connects the German market with Switzerland, Belgium and The Netherlands. It runs across Germany from Bocholtz and Eynatten at the Dutch respectively Belgian borders to Wallbach at the Swiss border, where the TENP pipeline connects to the Transitgas pipeline. The TENP pipeline serves also the local market and is a major gas infrastructure for the NCG market area."
Nord Stream
 Read more: Nord Stream
Read more: Nord Stream
Trans Adriatic Pipeline (TAP)

Read more: TAP
EastMed - The Eastern Mediterranean pipeline
Read more: EastMed